HAB Resources
Report a Bloom
HAB Monitoring Program Overview
Monitoring and Sampling Summary and Key Resources
Health Advisory Signs and Posting Guidance
Informational Posters and Brochures
HAB Monitoring Program Overview
The Harmful Algal Bloom (HAB) Monitoring Program is implemented by several state agencies to carry out the responsibilities and procedures outlined in the HAB Strategic Response Plan (SRP).
These agencies include, but are not limited to:
- Nevada Division of Environmental Protection (NDEP)
- Nevada Division of State Parks (NDSP)
- Nevada Division of Wildlife (NDOW)
- Nevada Department of Agriculture (NDA)
- Nevada Office of State Epidemiology (OSE)
The task force executes the HAB Monitoring Program goals through regular monitoring, sampling, and interagency communication. Monitoring and sampling consists of visual assessment in the field, desktop analyses of satellite data, and laboratory analysis of water samples. Monitoring and sampling are typically conducted during warmer summer months.
Monitoring and Sampling Summary and Key Resources
| Recommended Actions and Resources | |
|---|---|
| Step 1: Surveillance and General Awareness | Participating agencies (NDEP, DNSP, NDOW, NDA) should visually monitor public waterbodies for potential HABs during peak recreation season. Responding agencies can use general awareness signs to inform the public about HABs. Resources: |
| Step 2: Reporting the Discover of a Potential HAB | Reports of potential HABs should be made through the HAB reporting tool (coming soon), and any potentially related human or animal illnesses should be made to NDHHS, NDA, or NDEP:
NDEP staff will evaluate reported HABs and deploy sampling and health advisories as appropriate. Resources: |
| Step 3: Interagency Responses, Coordination and Communication | NDEP will evaluate reported potential HABs and coordinate with the appropriate agency staff in responding to the HAB. When potential HAB-related human or animal illness are reported, OSE staff will follow up to collect additional information and provide assisstance. Resources: |
| Step 4: Field Screening | Responding agency staff can use field screening methods to determine if cyanobacteria and cyanotoxin indicators are present. As necessary, samples may be collected for lab analysis at this step (refer to Step 5). Field screening methods includes visual indicators, jar test, and stick test. If field screening methods confirm the presence of HAB indicators or a HAB-related illness is suspected, NDEP will submit a recommendation for a HAB Watch advisory and corresponding advisory signage to be posted at the waterbody to inform recreationalists of potential health risks. Resources: |
| Step 5: Cyanotoxin Sampling | If field screening methods confirm the presence of HAB indicators or a HAB-related illness is suspected, NDEP will recommend cyanotoxin sampling. NDEP will coordinate with responding agency staff to collect cyanotoxin samples for submittal to NDEP. Resources: |
| Step 6: Issuing Health Advisories | If analyses or observations meet or exceed Health Advisory Threshold Levels, NDEP will submit a recommendation to the OSE to issue the apporpriate health advisory. NDEP will recommened the corresponding advisory signage to be posted, and will communicate and coordinate with the appropriate agencies. Resources: |
| Step 7: Continue Monitoring and Revise Advisory as Needed | While a waterbody is under an advisory, ongoing visual monitoring and field screening will be conducted by the responding agency. If observations suggest that the HAB is significantly increasing or decreasing, then the responding agency will communicate with NDEP to determine wether follow-up cyanotoxin samples should be collected. If follow-up cyanotoxin samples are collected, NDEP will submit a reccomendation to OSE to revise the advisory as needed. Resources: |
| Step 8: Remove Advisories and Routine Monitoring | Once visual indicators and/or cyanotoxin concentrations are below the Health Advisory Threshold Levels for a minimum of two consecutive weeks, NDEP will submit a recommendation to OSE to remove the health advisory signage. Resources: |
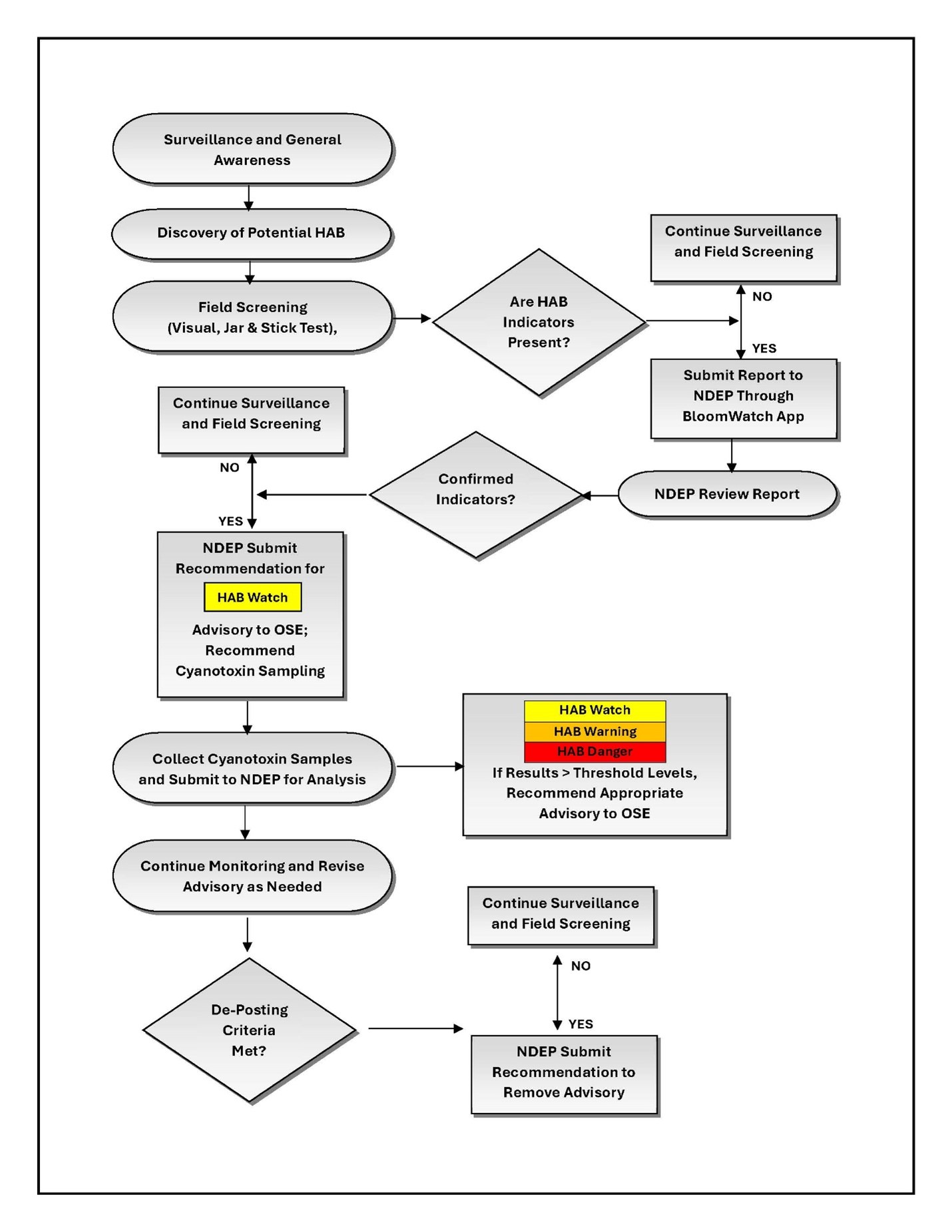
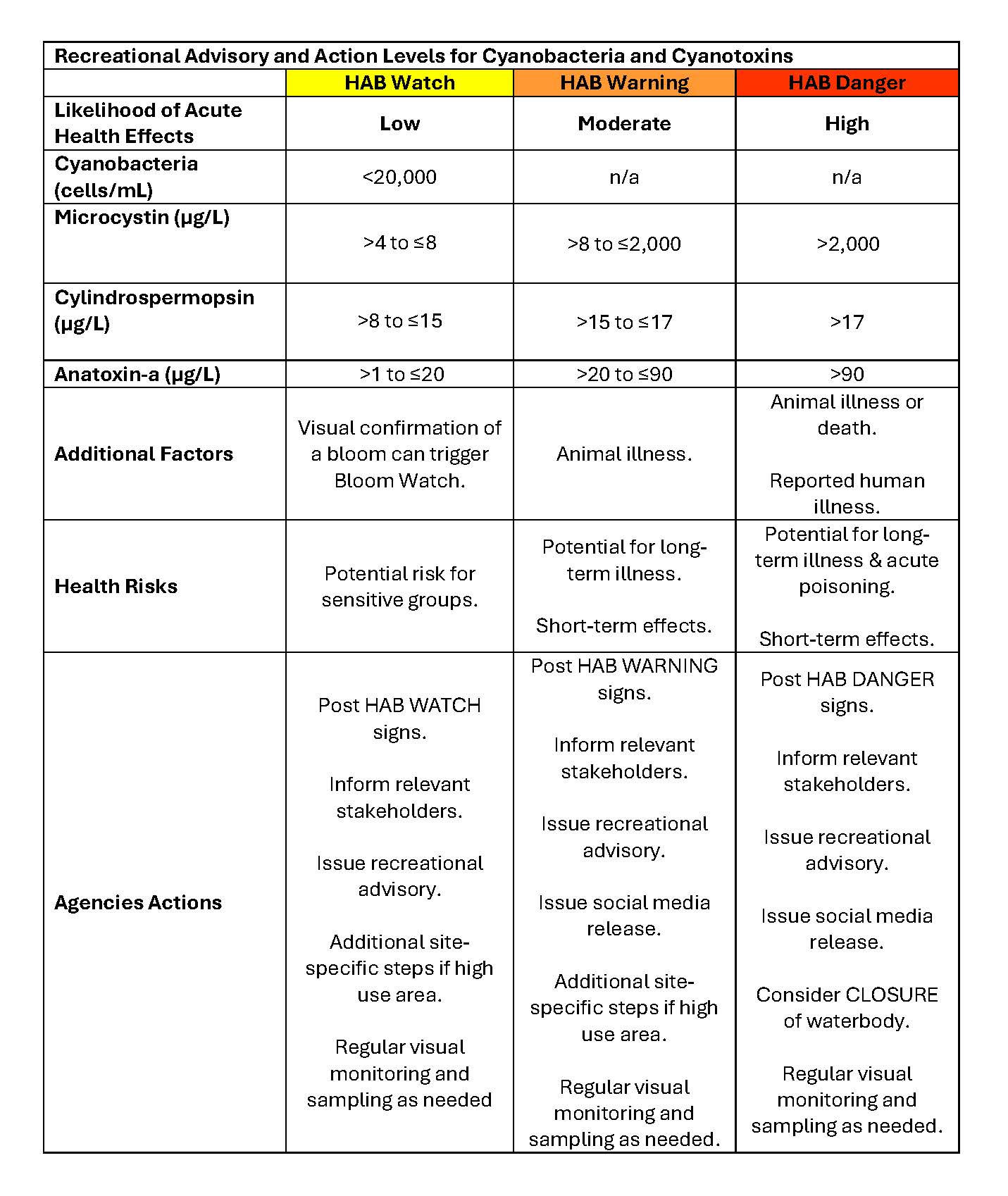
Table 1: Recreational Advisory and Action Levels for Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins |
|---|
 |
Health Advisory Signs and Posting Guidance
Health advisories can be issued based on visual confirmation, satellite imaging confirmation, and/or laboratory analysis of cyanotoxin concentrations. The level of health advisory is determined by how the HAB is verified and the level of cyanotoxins found in water samples (Table 1). The presence of HABs and related data will be shared with participating agencies as well as the public. The OSE will issue or lift health advisories and encourage field staff to share this information by posting the provided health advisory signage.
For more information on the most recent data and advisories please visit the HAB Data webpage and the HAB OSE Dashboard.
Informational Documents, Posters and Brochures
- Strategic Response Plan (PDF)
- Standard Operating Procedures (PDF)
- Recreational Threshold Advisory Rationale (PDF)
- Guidance for HABs in Nevada Brochure (PDF)
- Health Advisory Signs (PDF)
- Be Algae Aware poster (PDF)
Report a Bloom
Report a possible bloom to the Biological Assessment and Monitoring Branch
Join the HAB Listserv!
For weekly updates on HAB data and health advisories, please join the Nevada HABs e-mail list by navigating to the bottom of this webpage and clicking "Get Notices" and selecting "Nevada Harmful Algal Bloom Updates" from the dropdown menu, or by sending an e-mail directly to NEVADAHABS-subscribe-request@LISTSERV.STATE.NV.US
References
https://www.cdc.gov/habs/index.html
https://www.cdc.gov/habs/illness-symptoms-freshwater.html
https://www.epa.gov/nutrientpollution/help-prevent-nutrient-pollution
https://www.noaa.gov/what-is-harmful-algal-bloom
https://nvose.org/programs/environmental-health/harmful-algal-blooms-eh/
