Caselton Mine Area and Mill Site, Lincoln County
Multistate Trust Information
Detailed information is provided in Chapter 3.S of the Multistate Trust Annual Progress Report, including ongoing cleanup efforts. This report is updated annually.
Note: although you can view the Annual Progress Report in a web browser, it is recommended that you download the PDF to see the bookmarks that provide easy access to individual sections.
For more information about the Multistate Trust, visit https://multistatetrust.org. The Multistate Trust publishes a detailed website for the Caselton Mine Area as of 2023 (https://caselton.greenfieldenvironmental.com).
Site History
The Pioche Mining District has a long history of silver, gold, lead, zinc, and copper production, starting in 1863. Significant development began in 1868 when San Francisco financier F. L. Pioche bought several mining claims and erected a smelter. The town of Pioche soon became the scene of a wild rush of prospectors and gained a reputation associated with tough gunmen and bitter lawsuits in the 1870s. More than $5 million in metals had been mined by 1872, and by 1900 Pioche was nearly a ghost town.
The Combined Metals Reduction Company (CMR) operated at the Site from 1924 to 1976. In 1941, the Caselton Mill was constructed, and after 1953 it was largely used to process ore.

Pioche, Lincoln County, NV.
Milling operations ceased in 1957 and by the early 1970s CMR filed for bankruptcy. In 1976, in connection with the bankruptcy proceedings, Kerr-McGee Corporation (Kerr-McGee) purchased the unpatented (exclusive rights to explore, develop and extract the minerals) and patented mining claims (exclusive title to surface and locatable minerals) from CMR. Some of these patented mining claims include the areas known as Treasure Hill, Caselton Heights, and the Caselton Mine Site, as well as certain other subsurface rights. The unpatented mining claims were allowed to lapse in 1993 and ownership of the unpatented mineral rights reverted to the Bureau of Land Management (BLM).
Kerr-McGee and its affiliates conducted wood-treating, manufacturing, mining, and other business operations at numerous sites around the country. By the mid-2000s, Tronox Inc. and its affiliates (Tronox) owned or were liable for the Caselton Site and many other sites contaminated by Kerr-McGee and its affiliates over decades of operations. Around the same time, Anadarko Petroleum Corporation (Anadarko) acquired Kerr-McGee’s valuable oil and gas assets for $18 billion. In 2009, Tronox, largely unable to pay for investigating or cleaning up the Kerr-McGee sites, filed for bankruptcy.
In 2011, the Multistate Environmental Response Trust (Multistate Trust) was created as part of a court-approved Tronox bankruptcy settlement involving the U.S. government, 22 state governments, and other parties to own, investigate, clean up and facilitate reuse of hundreds of former Kerr-McGee/Tronox sites in 31 states, including the former Caselton Mine Area (the Site). The Multistate Trust performs environmental actions under the oversight of and as approved by the Nevada Division of Environmental Protection (NDEP), as the lead agency for the Site. The beneficiaries of the Multistate Trust include the State of Nevada, represented by NDEP, and the United States, represented by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and BLM. Both NDEP and EPA, in consultation with the U.S. Department of Justice, must approve the sale, transfer, or disposition of all or any portion of the Site.
Site Cleanup
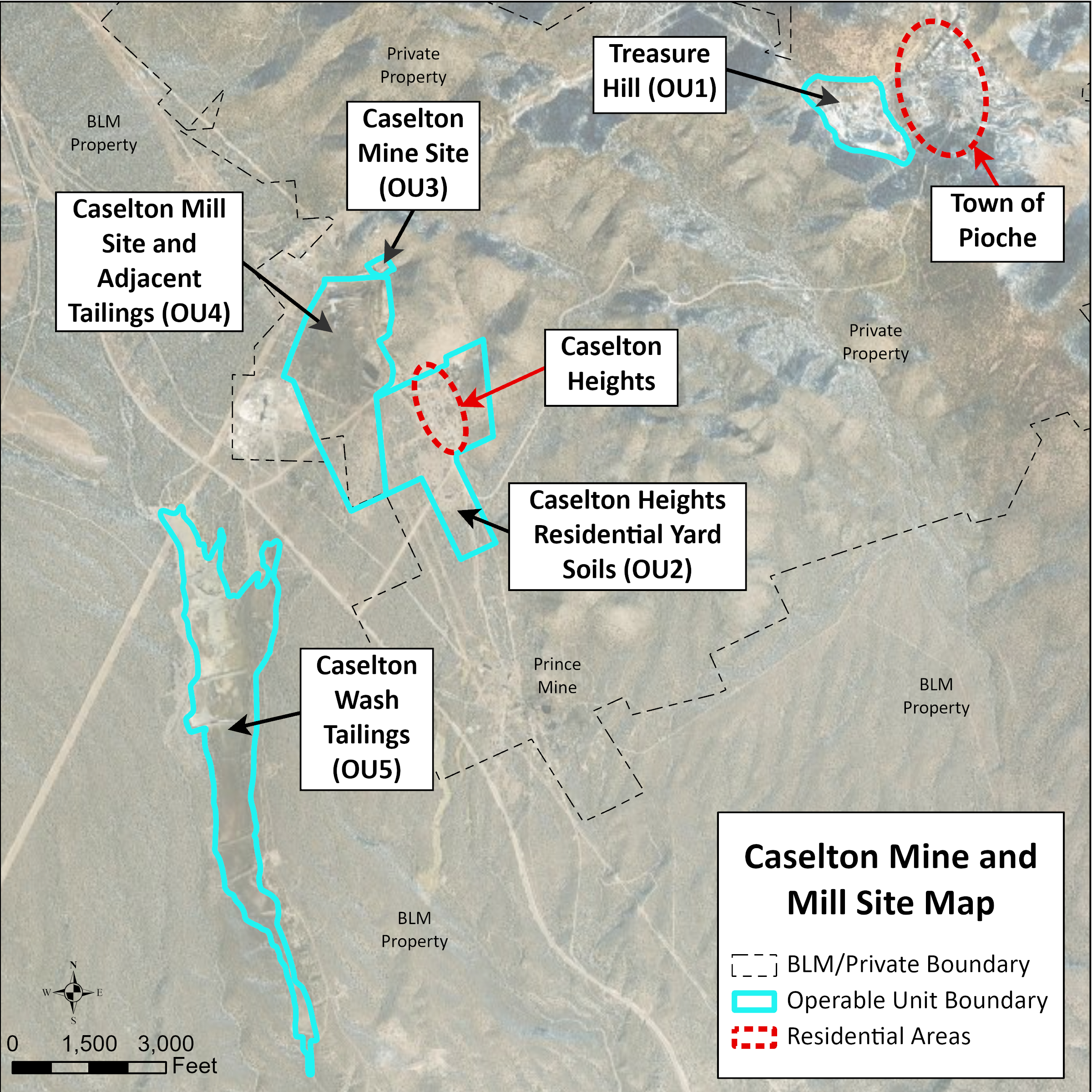
The Caselton Mine Area is located near Pioche, Nevada, along Highway 93, approximately 125 miles north of Las Vegas. The approximately 3,200-acre Site has been mined for silver, gold, lead, zinc, and copper. While mining operations have ceased, some structures remain.
For the purpose of investigating the different areas of the Site and developing appropriate cleanup goals and remedial strategies, the Multistate Trust and NDEP have divided portions of the Site into five distinct geographic locations. These areas are called “operable units” (OUs) in order to identify the specific areas where environmental actions may occur.
The five operable units (OUs) include:
- OU1: Treasure Hill
- OU2: Caselton Heights Residential Yard Soils
- OU3: Caselton Mine Site
- OU4: Caselton Mill Site and Adjacent Tailings
- OU5: Caselton Wash Tailings (Managed by BLM)
Together, OU3 and OU4, are also known locally as the Caselton Mine and Mill Site.
OU1: Treasure Hill
Investigations and Cleanup Actions:
- Collected background soil and waste rock samples
- Waste rock sample results were above risk-based cleanup levels for trespasser and recreators in this area.
- Stormwater and Sediment Transport Issues (Treasure Hill into the Town of Pioche)
- Collected 45 roadway sediment samples along Newark Street and Tank Road to evaluate the potential risk to the roadway worker of exposure to lead and arsenic contaminated sediment when cleaning roadways after flooding events.
- Determined that the potential risk of unacceptable exposure to contaminants by a roadway worker was low, because the frequency and duration of roadway sediment removal was minimal.
- Residential Yard Sampling (Town of Pioche residential properties closest to Treasure Hill)
- A total of 567 samples were collected and analyzed for lead and arsenic.
- 29 residential parcels, with existing houses, had lead and arsenic concentrations that exceed the risk-based cleanup action levels.
- The NDEP and Multistate Trust prioritized removal of lead and arsenic contaminated soils in residential yards along Tank Road, Newark Street, and Ely Street as an interim action.
- 18 of the 29 residential parcel property owners participated in the Residential Yard Soil Removal Action, completed in July 2022.
- Approximately 2,300 cubic yards of contaminated soil was removed from the residential parcels.
- A 5-year remedy review process will be conducted in 2027 to assess the effectiveness and protectiveness of the Residential Yard Soil Removal Action.
- Tank Road Parcel with Tailings (Assessor Parcel Number 001-111-21)
- Tailings identified on this property.
- Collected 40 samples.
- Multistate Trust, with approval from NDEP and the United States, supported Lincoln County’s acquisition of this property.
- Property may be suitable for long-term stormwater management following an investigation to evaluate cleanup and stormwater options, including development of implementation costs.
- Implementation of environmental actions is ongoing.
OU2: Caselton Heights Residential Yard Soil Investigation
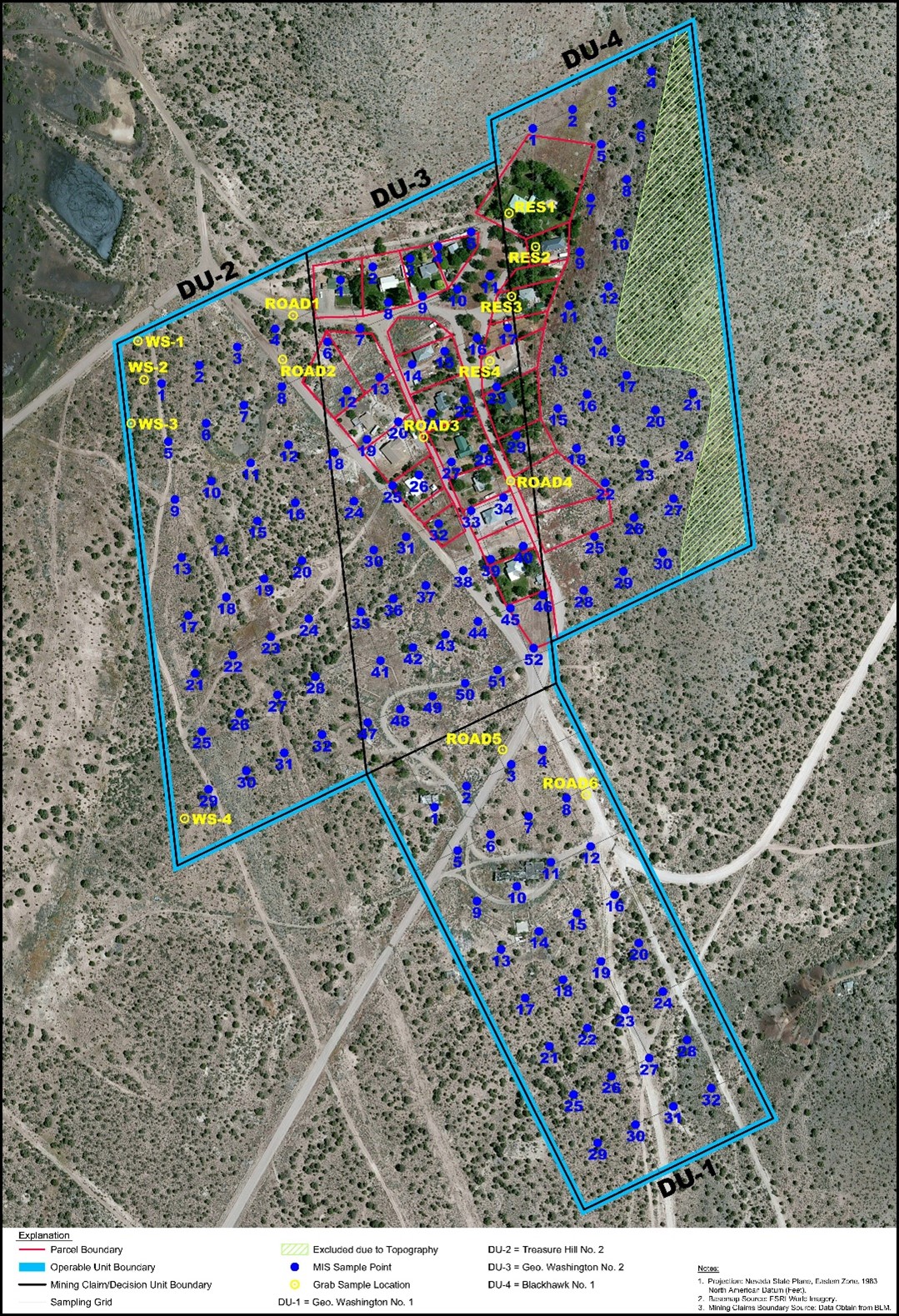
Investigations and Cleanup Actions:
- Developed a sampling plan for residential and unoccupied parcels.
- Collected 128 samples and analyzed for metals.
- Sample results were below the risk-based cleanup levels and considered safe for residential uses, thus no cleanup action was warranted.
- Land beneath the homes was transferred from the Multistate Trust, with approval from its beneficiaries, to the individual property owners or Lincoln County in 2018.
OU3: Caselton Mine Site
Investigations and Cleanup Actions:
- OU3 is not part of the current environmental hazard investigations; therefore, no investigation or cleanup is anticipated.
- The Multistate Trust secured access to the mine shaft to prevent trespassing.
OU4: Caselton Mill Site and Adjacent Tailings
Investigations and Cleanup Actions:
- Collected grab soil samples for background and mill site delineation.
- Grab soil sample results were above risk-based cleanup levels for future industrial workers, recreators, and ecological receptors.
- Separated the area into OU4A and OU4B to facilitate more efficient assessment and cleanup of the more heavily impacted area around the mill site (OU-4A) and less impacted area south of the mill site (OU-4B).
- Implementation of environmental actions is ongoing.
OU5: Caselton Wash Tailings (Managed by BLM)
Between 1986 and 2010, a number of environmental site assessments, investigations and evaluations were performed by Kerr-McGee, BLM, and U. S. Army Corps of Engineers. Recent and current investigations include:
- Groundwater Assessments in the Caselton Wash
- In 2017, the Multistate Trust drilled two borings to determine the depth of groundwater beneath the tailings (CM-MW-1 and CM-MW-2).
- Groundwater was not encountered at CM-MW-1. Total depth of boring was 483 feet below ground surface (bgs).
- Groundwater was encountered in CM-MW-2 at a depth of 328 feet bgs. A well was installed and sampled for 2 years. Metals concentrations were low to non-detect (below drinking water standards).
- Modeling by University of Nevada, Reno to determine potential for leaching of contaminants to groundwater.
- Soil Investigations in the Caselton Wash
- In 2019, the Multistate Trust collected 160 soil samples over an 8-mile length downstream of the Caselton Wash Tailings Ponds.
- Risk assessment evaluation determined that wash soils are not expected to result in unacceptable risk to recreators.
- While there is potential risk to ecological receptors, the actual risk is likely overestimated and is not likely to adversely affect the ecological receptors.
- BLM is performing a comprehensive remedial investigation and feasibility study to evaluate watershed impacts from OU4 and OU5 contamination.
For questions or additional information, please contact the NDEP's Bureau of Corrective Actions at: (775) 687-9368.
Portions of site history from Pioche Chamber of Commerce: https://piochenevada.com/history/
Find It:
