- Sustainable Nevada: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
- Sustainability
Sustainability
What is sustainability?
Sustainability is the ability to create and maintain the conditions under which humans and nature can exist in productive harmony to support present and future generations. It involves meeting our resource, development, water, and energy needs while not compromising natural systems or quality of life. There are many topics related to sustainability, including, but not limited to, sustainable materials management (SMM), natural resource conservation, and climate action.
- Sustainable Materials Management
- Water Conservation
- Energy Conservation & Energy Efficiency
- Climate Action
- Become More Sustainable
Sustainable Materials Management (SMM)
The overarching goal of any sustainable practice is to ensure that people have sufficient resources to meet today’s needs as well as the needs of the future. The SMM framework helps to achieve this goal by focusing on ways to use materials in the most productive way and by emphasizing waste reduction.
The SMM framework views waste as a system inefficiency, and for the wastes that cannot be avoided, this approach looks for ways to use those wastes as resources and inputs to new processes. Thus, SMM promotes a circular system with a focus on reducing negative impacts to the environment and public health by reducing waste, reusing materials, recycling, and composting. Landfilling is viewed as a last resort.
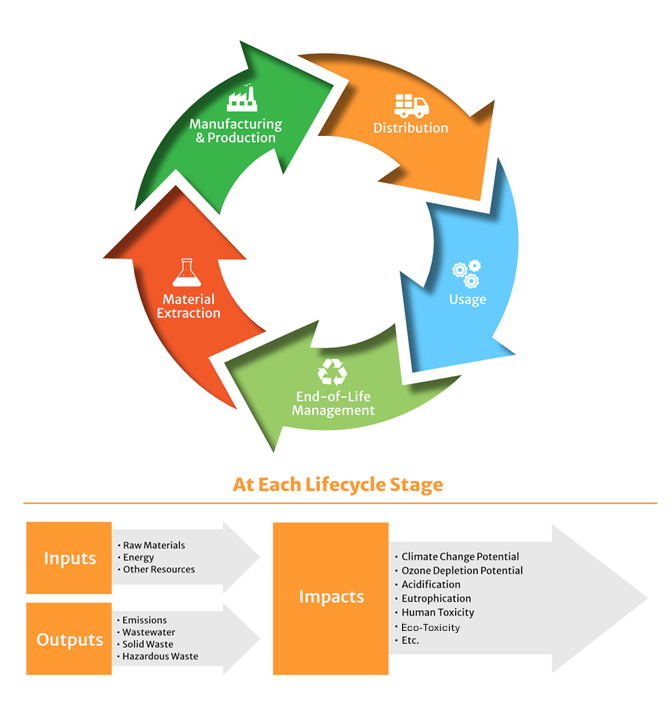
Additionally, rather than focusing solely on end-of-life management, the SMM framework takes a step back and looks at whole systems and lifecycles of materials. SMM involves understanding material flows and the associated inputs (e.g., raw materials, energy, water) and outputs (e.g., waste streams, emissions, by-products) at each stage of a product’s lifecycle. Viewing products and materials through this lifecycle perspective helps us understand that when a product ends up in a landfill, more impacts are occurring than just the disposal of that particular item. When a product is thrown away without making the most productive use of it, all of the upstream inputs are lost, and the associated environmental impacts are intensified.
Water Conservation
Water conservation is a major sustainability topic for the state of Nevada. Due to our dry desert climate and ongoing drought conditions in the Colorado River Basin, it is crucial we reduce our water usage to secure a dependable water supply for Nevada’s future. While the quantity of water is important, so is the quality of Nevada’s water. We need to keep pollutants, such as trash, chemicals and microplastics, out of our waterways to ensure clean water for our residents, wildlife, and ecosystems.
Additionally, water and energy are tied together. Often called the water-energy nexus, energy is needed to treat and deliver water. Therefore, reducing our water usage can help lower our energy needs. Lowering the energy demand can help reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions related to climate change.
Energy Conservation & Energy Efficiency
Energy conservation and energy efficiency go hand-in-hand. Energy conservation is focused on reducing our energy usage with the goals of reducing our carbon and ecological footprints and saving money. Energy efficiency involves using less energy to accomplish the same task or job. This is often accomplished through installing more energy efficient appliances and using building materials that reduce the energy demand for heating and cooling.
All forms of energy generation have environmental impacts, but the magnitude and types of impacts vary depending on the resources used for generation. Therefore, it’s important to be smart about how we use energy and take steps to reduce wasting energy. According to the EPA, here are some environmental impacts associated with energy production:
- Greenhouse gases (GHG) and other air pollutants are emitted, especially when a fossil fuel is burned
- Water resources are used to produce steam or provide cooling
- Wastes, which may be toxic or hazardous, are generated
- Land and ecosystems are impacted from resource extraction, power generation, and physical infrastructure such as power lines
Climate Action
Climate action involves finding and implementing solutions to address climate change and its associated impacts. As a foundation to Nevada’s effort to build a climate-resilient future, the Nevada Department of Conservation and Natural Resources (DCNR) and the Nevada Governor’s Office of Energy (GOE) released an updated and expanded Nevada Statewide Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions Inventory and Projections Report (Nevada Statewide GHG Inventory). Read more about the GHG Inventory and Projections Report.
Become More Sustainable
Whether you are a Nevada resident, business, educator, or a government agency, we all have a role to play in improving sustainability across our state.
Businesses - Explore Sustainable Practices
Residents - Become More Sustainable at Home
Educators - Teach Sustainablility Topics
Government Agencies - Become a Sustainability Leader in Your Community